The main product of cellular respiration is ATP. Identify which molecule in the reaction will be oxidized and which molecule will be reduced.

Amazing Info About Describe The Role Of Oxygen In Cellular Respiration 2022 Lisbdnet Com
Loss of an electron and a deprotonation event ie.

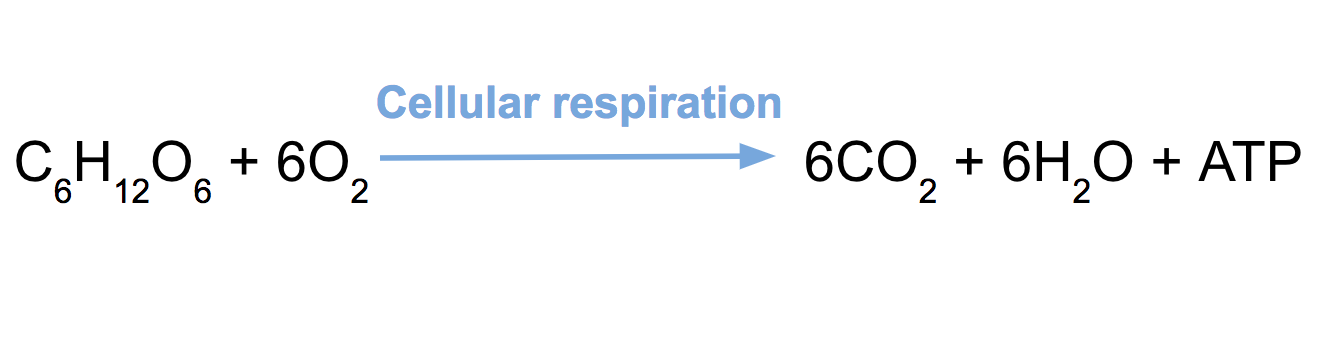
. An important part of cellular respiration is the transfer of electrons. Oxidation and reduction is about the transfer of electrons. The reaction pictured below is an oxidation-reduction reaction in the citric acid cycle in which the energy-carrier molecule NADH is generated.
Correspondingly what is cellular respiration and where does it occur. During aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming ATP that can be used by the cell. 10 Which of the choices below describes the pathway of cellular respiration the complete oxidation of glucose.
Describe the cellular regions where glycolysis the Krebs. Up to 24 cash back Aerobic Respiration. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products.
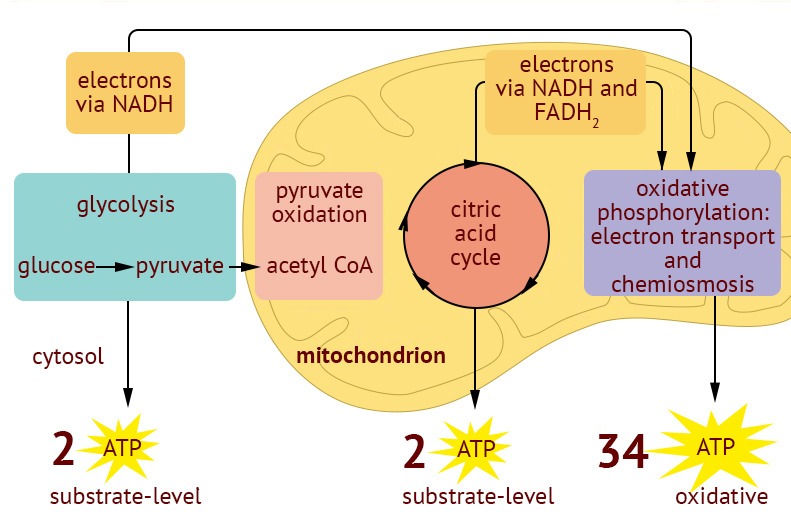
In which reactions of cellular respiration and fermentation does substrate-level phosphorylation occur. In the presence of oxygen an increase in the amount of ATP in a cell would be expected to. Reduction a molecule gains electrons.
A type of cellular respiration defined as the energy metabolism in the presence of oxygen. Oxidation a molecule loses electrons. Glucose a six-carbon sugar enters the cell by passive transport and is primed and converted into glucose three-phosphate which requires two ATP molecules.
In the first two phases of cellular respiration glycolysis and Krebs cycle electrons are transferred to. Recall that a redox reaction is simply shorthand for an oxidation-reduction reaction. In the enzymatic reaction shown below both types of events occur within the substrate molecule.
Define oxidation and reduction. Describe the role of NAD and the electron transport chain during respiration. As we explore the chemical reactions that occur during cellular respiration it will be useful for you to be able to recognize the difference between an oxidation event ie.
Cellular respiration is the oxidation of this molecule The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain These molecules are reduced in the citric acidKrebsTCA cycle Total number of ATP molecules produced by the end of pyruvate oxidation. In this process the oxidation of organic compounds of high energy content producing carbon dioxide and water and the release of energy is used. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high.
Cellular respiration is a phenomenon that basically consists of the process of extracting chemical energy accumulated in the molecules of diverse organic substances such as carbohydrates and lipids. Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down glucose release the stored energy and use it to make ATP. Electron carriers in cellular respiration.
Loss of a proton. In an oxidation reaction electrons are lost. Use the acronym OIL RIG to remember this O xidation I s L oss R eduction I s G ain.
That means that during cellular respiration some molecules in our cellular respiration. Waste products include carbon dioxide and water. Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically using oxygen or anaerobically without oxygen.
Pyruvate is modified by removal of a carboxyl group followed by oxidation and then attached to Coenzyme A. Which statement accurately reflects what happens to a glucose molecule during the initial 5 phases of glycolysis. Photofructokinase is an allosteric enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose -6-phosphate to fructose 1 6-biphosphate an early step of glycolysis.
Both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle Which of the following statements describes what happens to a molecule that functions as the reducing agent electron donor in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction. Place a single answer choice in each box. The gain or loss of electrons.
In a reduction reaction electrons are gained. Explain how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges. The basic terms.
Oxidize NADH to NAD. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts. How pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to acetyl CoA so it can enter the citric acid cycle.
Science Biology library Cellular respiration Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle. The remaining four steps involve splitting the six. Oxygen and glucose are both reactants in the process of cellular respiration.
A lipolysis glycogenolysis beta oxidation B glycogenesis lipogenesis electron transport chain C glycolysis citric acid Krebs cycle electron transport chain oxidative phosphorylation.
Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration Biology Quizizz

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica
0 Comments